The Infertility Website
Female Infertility Articles
We are the top source for complete info and resources for Female Infertility Articles on the Internet.
MESA or TESA? (PDF, 115 KB) Human Reproduction, 1996. Weight loss in obese infertile women results in improvement in reproductive outcome for all forms of fertility treatment. Myoma treatment In general, small and asymptomatic myomas do not require treatment, but the patient should be periodically monitored.
Following his lecture on laparoscopic appendectomy, the president of the German Surgical Society wrote to the Board of Directors of the German Gynecological Society suggesting suspension of Semm from medical practice. Once the follicular diameter reaches 18 mm and the E2 level is below 2000 pc/mL, ovulation is triggered by the administration of hCG (10,000 IU IM). Microscopic Technique for Reversal of Vasectomy. (PDF, 3 MB) Surgery, gynecology & obstetrics, 1976. Transmission of Male Infertility to Future Generations: Lessons from the Y Chromosome. (PDF, 303 KB) Human Reproduction Update, 2002. Inhibin B levels have been reported to decrease with increasing weight, which results in decreased Sertoli cells and sperm production.
Much more Resources For Unexplained Infertility Treatment in India
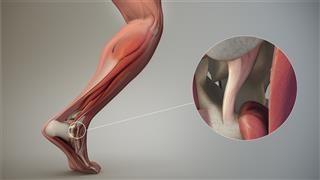
Much more Resources For Female Infertility Articles
Legal, cultural and religious inquiries have limited the available choices in some countries, such as the use of donor sperms or oocytes. Pregnancy Caused by Sperm from Vasa Efferentia. (PDF, 1 MB) Fertility and Sterility, 1988. The Disappearing Y Chromosome – “I Told You So!” (PDF, 266 KB) Human Reproduction, 1997. This indicates whether the fallopian tubes are open or blocked. A small incision is made in the abdomen, and a thin, flexible microscope with a light at the end, called a laparoscope, is inserted through it. In the United Kingdom, it is estimated that one in six couples would complaint of infertility [3].
Right here are Some Even more Resources on Female Infertility Articles
Semen quality Semen is initially a coagulum that liquefies in 5-25 minutes due to prostatic enzymes. Previous sterilization treatment: In women who have chosen to have their fallopian tubes blocked, the process can be reversed, but the chances of becoming fertile again are not high. A high serum estradiol level (greater than 60 to 80 pg per mL [220 to 294 pmol per L]) in conjunction with a normal FSH level has also been associated with lower pregnancy rates.
More Info About Infertility Endocrinology
Patients who do not achieve ovulation after three to six cycles should be referred to an infertility specialist for further treatment. Overheated testicles: Causes include an undescended testicle, a varicocele, or varicose vein in the scrotum, the use of saunas or hot tubs, wearing tight clothes, and working in hot environments. 1 Among couples 15 to 44 years of age, nearly 7 million have used infertility services at some point. Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk of infertility in both men and women, and it may undermine the effects of fertility treatment. Sperm counts can fluctuate, so that several samples may be necessary. Many more couples, however, experience involuntary childlessness for at least one year: estimates range from 12% to 28%.[4] Male infertility is responsible for 20–30% of infertility cases, while 20–35% are due to female infertility, and 25–40% are due to combined problems in both parts.[2][5] In 10–20% of cases, no cause is found.[5] The most common cause of female infertility is ovulatory problems, which generally manifest themselves by sparse or absent menstrual periods.[6] Male infertility is most commonly due to deficiencies in the semen, and semen quality is used as a surrogate measure of male fecundity.[7] Women who are fertile experience a natural period of fertility before and during ovulation, and they are naturally infertile for the rest of the menstrual cycle. Microsurgical Reversal of Tubal Sterilization: Factors Affecting Pregnancy Rate, with Long-term Follow-up. (PDF, 2 MB) Obstetrics & Gynecology, 1984. Primary vs. secondary infertility[edit] Primary infertility is defined as the absence of a live birth for women who desire a child and have been in a union for at least 12 months, during which they have not used any contraceptives.[14] The World Health Organisation also adds that 'women whose pregnancy spontaneously miscarries, or whose pregnancy results in a still born child, without ever having had a live birth would present with primarily infertility'.[15] Secondary infertility is defined as the absence of a live birth for women who desire a child and have been in a union for at least 12 months since their last live birth, during which they did not use any contraceptives.[15] Thus the distinguishing feature is whether or not the couple have ever had a pregnancy which led to a live birth. Regression of Metastases after Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma. (PDF, 1 MB) British Journal of Urology, 1975. Government, the Department of Defense, or the Department of the Air Force. 35. In women aged under 40 years who have not conceived after 2 years of regular unprotected intercourse or 12 cycles of artificial insemination (where 6 or more are by intrauterine insemination), offer 3 full cycles of IVF, with or without ICSI.
Previous Next
See also
Infertility Treatment First Step
Infertility in China
Rate of Infertility